您现在的位置是: 首页 > 励志格言 励志格言
_高中英语句子成分详细分析例句
tamoadmin 2024-09-07 人已围观
简介1.分析高中英语句子成分结构?2.高中英语 句子成分3.高中英语重点句式讲解 让你吃透“强调句”4.英语句子成分5.英语句子成分应当如何判断?高中常见句式结构及其用法Worse still, it is a waste of time.?更糟的是,这是浪费时间。除了Worse still作状语以外,就是一个典型的“主系表”结构的简单句:it 主语;is 系动词;a waste of time 表语
1.分析高中英语句子成分结构?
2.高中英语 句子成分
3.高中英语重点句式讲解 让你吃透“强调句”
4.英语句子成分
5.英语句子成分应当如何判断?高中常见句式结构及其用法
Worse still, it is a waste of time.?更糟的是,这是浪费时间。
除了Worse still作状语以外,就是一个典型的“主系表”结构的简单句:
it 主语;
is 系动词;
a waste of time 表语;(这个名词短语中的核心名词是waste,a 是一个限定词,of time 是后置定语;再细分介词短语of time,time 是介词of 的宾语)
补充说明:
英语的谓语有两类“复合谓语”(即不是由单个动词构成的谓语)
1. 系动词+表语 (既不能没有系动词,也不能没有表语)
2. 情态动词+原型动词 (情态动词不能单独作谓语,因为这样谓语不完整,意义不明确;而去掉情态动词后,句子的含义也跟原来不同,所以只有二者配合才是完整的谓语)
分析高中英语句子成分结构?
The annual race主语 (titled "walk on water,"分词定语) is谓语 an assignment表语( required to pass Architecture Professor Jaime Canes'class.分词定语)
名为 "walk on water的一年一度的比赛是一项任务(一项需要通过建筑教授Jaime Canes的课程的任务)
高中英语 句子成分
ear的主语不是fact,是people。
句子的主干是This idea is supported by
the fact.而后面的that...一直到longer,这个从句是fact同位语从句,用来说明这个fact(事实)是什么。
这个同位语从句的主语是people,谓语是ear to live longer。people后的who引导的从句是用来修饰people的定语从句,people,什么样的people更聪明的
people。
这句话的意思是:这个观点被一个事实所支撑,那就是更聪明的人活的时间更长。
高中英语重点句式讲解 让你吃透“强调句”
1,disneyland can be found everywhere 这是一个简单句 disneyland 是主语 can be found 是谓语 everywhere是地点状语2 you can meet any cartoon character you like at disneyland 这是一个复合句 you 是主语 can meet 是谓语 any 是定语 cartoon是定语 character是宾语 后面是省略that的定语从句 在这个定从中 you 是主语 like 是谓语 省略的that是宾语at disneyland 是主句的地点状语3tourism develops where a disneyland is built.这是复合句tourism是主语 develops 是谓语 where引导的是地点状语从句在这个状从中 a disneyland 是主语 is build是谓语 4 Wollywood is in the mountains in the southeastern USA. 这是简单句 wollywood 是主语 is 是系动词 in the mountain 是表语 in the southeastern usa是定语5 Country music singers perform in Dollywood throughout the whole year .这是简单句 country music是定语 singers 是主语 perform 是谓语 in dollywood是地点状语从句 throughout the whole year 是时间状语从句6 Dollywood has the only electric train still working in the USA . 只是简单句dollywood 是主语 has 是谓语 only是定语 electric是定语 train 是宾语 still是状语 working in the usa 是现在分词短语作定语 in the usa 是 现在分词的状语 7Visitors to Camerot park can taste candy like the candy made in ancient England.这是简单句vistors是主语 to camerot park 是定语 can taste 是谓语 candy是宾语 like到结尾是介词短语作定语 在这个短语中 candy是介宾 made 到结尾是过去分词短语作定语 在这个分词短语中in ancient england 是地点状语 修饰made 8 Camerot park has the oldest roller coaster in the word. 这是简单句camerot park 是主语 哈斯是谓语 oldest是定语 roller coaster是宾语 in the world 是定语 9 Camerot park has an ancient english farm. 这是简单句cameraot park 是主语 has 是 谓语 ancients 定语 english是定语 farm 是宾语10 Camerot park has places for visitors to watch and maybe take part in sword fighting.这是简单句camerot park 是主语 has 是谓语 places是宾语 for到结尾是不定式的复合结构 作定语在这个不定式短语中 visitors 是不定式的逻辑主语 and是并列连词 并列两个不定式 maybe是副词作状语 take part in 是并列的不定式 公用一个to 公用一个逻辑主语 sword fighting 是take part in 的宾语。
分
英语句子成分
强调句型的构成是:It is (was) + 被强调部分+ that (who) + 句子的其他成分。被强调的部分放在 It is (was) 之后,其它部分置于that之后。被强调部分可以是主语,宾语,表语或状语。强调的主语如果是人,可以由who代替that。
1. 被强调的成分举例:
原句:Tom found my pen in the classroom yesterday.
强调主语:It was Tom who / that found my pen in the classroom yesterday.
强调宾语:It was my pen that Tom found in the classroom yesterday.
强调地点状语:It was in the classroom that Tom found my pen yesterday.
强调时间状语:It was yesterday that Tom found my pen in the classroom.
2. 强调句型的一般疑问式:
直接把is或was提到it之前即可。例如:
Was it Tom that found your pen in the classroom yesterday?
3. 强调句型的特殊疑问式:
特殊疑问词+ is (was) it + that +句子的其他成分。特殊疑问词即是被强调的成分。例如:
Who was it that found your pen in the classroom yesterday?
4. that (who) 有时可以省略:
这种强调句型中的that或who有时可以省略。例如:
It was my brother (that / whom) you saw the other day.
5. 强调原因状语从句要注意:
若从句由as或since引导,强调时则改为because,这是因为,because引导的原因从句表示的意义非常强烈,符合强调句的目的。例如:
As she got up late, she missed the first bus. 变为:
It was because she got up late that she missed the bus.
6. 强调句的否定转移:
有些否定句在变成强调句时,要把否定转移到被强调的词语之前。尤其是“not... until...”句式的强调要特别注意。例如:
He didn't realize his mistake until the teacher had told him. 变为:
It wasn't until the teacher had told him that he realized his mistake.
注意 在强调句式中,虽然not被提前,但“not... until...”句型不要倒装。
高考中强调句型考查热点
考点一:强调句型的基本结构
强调句型“It is / was + 被强调的成份 + that + 其他成份”用来强调主语、宾语和状语等成份。that只起连接作用,不作成份,但不能省略。有时强调的部分比较特殊,如主语从句、状语从句、名词、不定式短语、V-ing的复合结构等。如:
It was in the library that I saw her yesterday. 我昨天正是在图书馆见到她的。
考点二:特殊句式中的强调句型
1. 如果强调的是特殊疑问句中的疑问词,表示“到底”、“究竟”等语气时,就用如下结构:
“特殊疑问词 + is / was + it + that + 该句的其余部分”。如:
How is it that you usually go to work? 你通常是怎样去上班的?
2. 在强调“not... until”结构中由until所引导的短语(或从句)作时间状语时,要用固定的强调句型:“It + is / was + not until... + that + 该句的其余部分”,that所引导的从句中的谓语动词用肯定式。如:
His father didn't come back from work until 12
o'clock. = It was not until 12 o'clock that his father came home form work. 直到12点他的爸爸才下班回家。
考点三:强调句型与时间状语从句、定语从句的判断
强调句型要注意和it代表时间、距离、温度、自然现象、具体事物或人物等时所构成的各种句型的区别。试比较:
It was on March 1 that I had my hair cut. (强调句)
It was March 1 when I had my hair cut. (后面是定语从句)
判断是否是强调句,可用“还原法”。如果还原为一般句式后,句子各种成份完整,则是强调句。否则不是。如第一句可还原成:I had my hair cut on March 1.
考点四:偶尔考查谓语动词的强调句式
英语中常用助动词do、does或did强调谓语。如:
He did go to the airport yesterday, but he didn't find you. 他昨天确实去了机场,但他没有找到你
英语句子成分应当如何判断?高中常见句式结构及其用法
“宾语+宾语补足语”结构构成了复合宾语,宾语与补足语之间具有逻辑上的主谓关系。例如,We all find him a nice boy.(him为宾语,a nice boy为宾语补足语)
间接宾语表示动作时对谁的或为谁做的。例如,He played us some light music.(us为间接宾语,some light music为直接宾语) 上面的例句也可以转换为 He played some light music for us.
同理,We often prepare some Chinese food for our friends也可以转换为 We often prepare our friends some Chinese food. 所以,在这句话中our friends为间接宾语,some Chinese food为直接宾语。
第三句话同样也可转换为This city has left the foreign tourists a deep impression.所以,在里面the foreign tourists是间接宾语,a deep impression 是直接宾语。
而第一句和第三句里面的介词for和on我认为则不充当成分,只是用来表示动作的对象。
至于第二句,We should not ask such personal questions as her age.我认为such personal questions做宾语,而as her age为宾语补足语,因为二者具有逻辑上的主谓关系,the personal question is her age 或者说 her age is the personal question.
我的参考资料来自《最新张道真高中英语语法》第十六章 句子成分,种类和主谓一致,第299页。希望对你会有帮助啦!
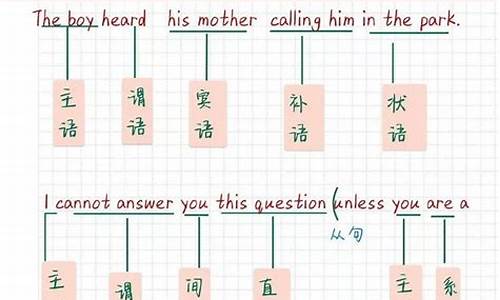
句子成分:英语句子成分分为七种:主语、谓语、宾语、定语、状语、表语、宾语补足语。1、主语是句子所要说的人或事物,回答是“谁”或者“什么”。通常用名词或代词担任。如:I’m Miss Green.(我是格林**)2、谓语动词说明主语的动作或状态,回答“做(什么)”。主要由动词担任。如:Jack cleans the room every day. (杰克每天打扫房间)3、表语在系动词之后,说明主语的身份或特征,回答是“什么”或者“怎么样”。通常由名词、代词或形容词担任。如:My name is Ping ping .(我的名字叫萍萍) 4、宾语表示及物动词的对象或结果,回答做的是“什么”。通常由名词或代词担任。如:He can spell the word.(他能拼这个词)有些及物动词带有两个宾语,一个指物,一个指人。指物的叫直接宾语,指人的叫间接宾语。间接宾语一般放在直接宾语的前面。如:He wrote me a letter . (他给我写了一封信)有时可把介词to或for加在间接宾语前构成短语,放在直接宾语后面,来强调间接宾语。如:He wrote a letter to me . (他给我写了一封信)5、定语修饰名词或代词,通常由形容词、代词、数词等担任。如:Shanghai is a big city .(上海是个大城市)6、状语用来修饰动词、形容词、副词,通常由副词担任。如:He works hard .(他工作努力)7、宾语补足语用来说明宾语怎么样或干什么,通常由形容词或动词充当。如:They usually keep their classroom clean.(他们通常让教室保持清洁) / He often helps me do my lessons.(他常常帮我做功课) / The teacher wanted me to learn French all by myself.(老师要我自学法语)☆同位语通常紧跟在名词、代词后面,进一步说明它的情况。如:Where is your classmate Tom ?(你的同学汤姆在哪里?)









